Every broker dealer has three departments:
Sometimes, middle-office and back-office are merged into the single department where the functions of middle-office are split between front-office and back-office.
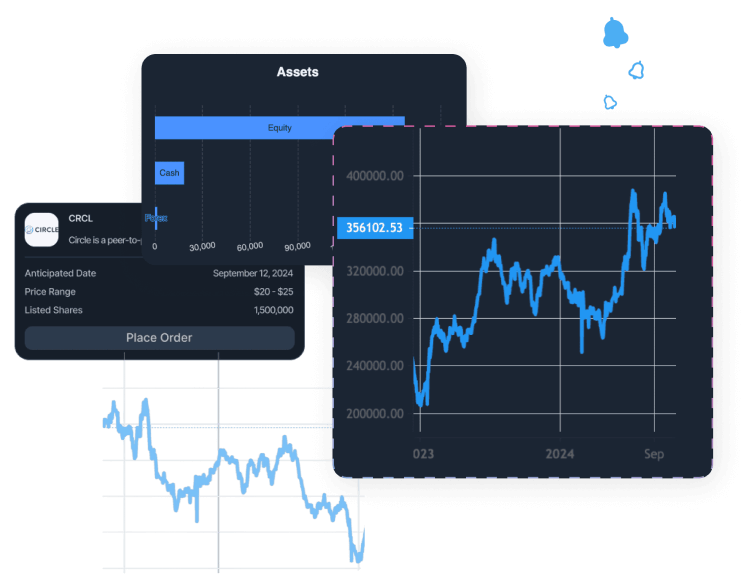
Front-Office is an application for end users (traders). In general, it should contain:
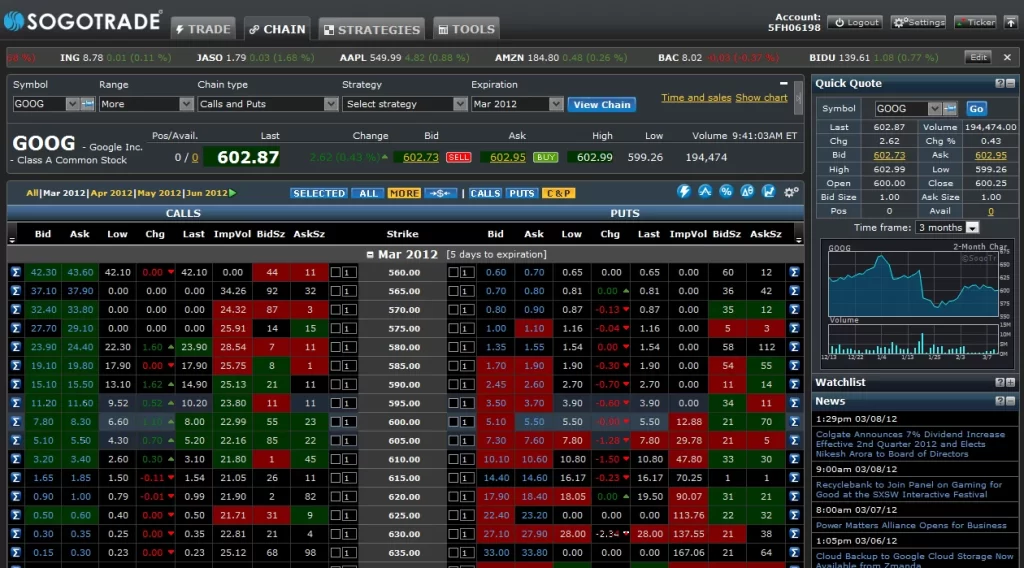
the following components can be included for research and analytical purposes:
In other words, that is a main entry point for retail customers of the brokerage firm where they can find any information related to the account and do a trade.
The main function of middle office can be described as “Order Control”. The order control system verifies accounts and securities while it goes into the execution.
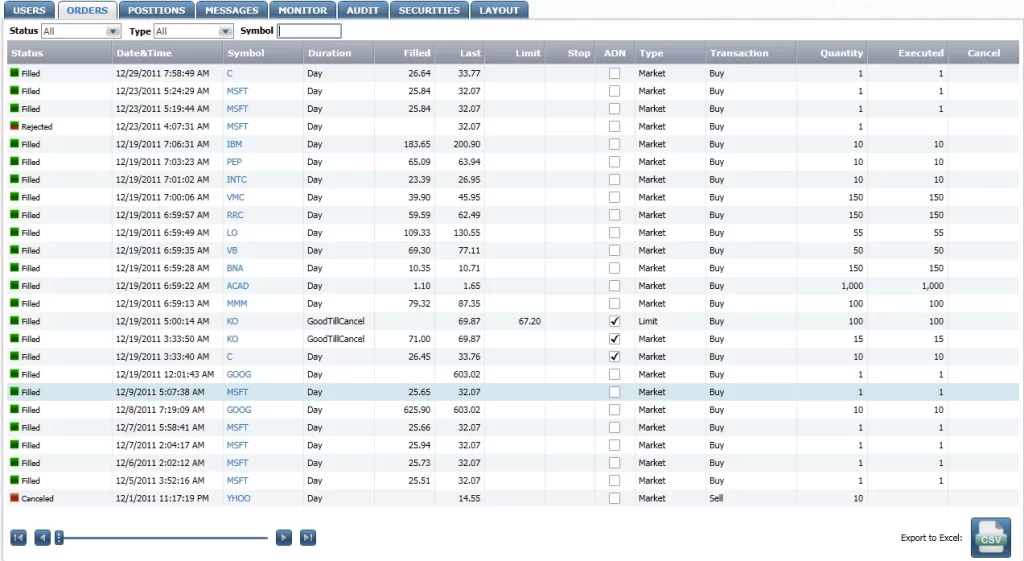
Back-Office takes the order from the point of execution to the settlement:
By Leonid Kurguzov, ETNA Software

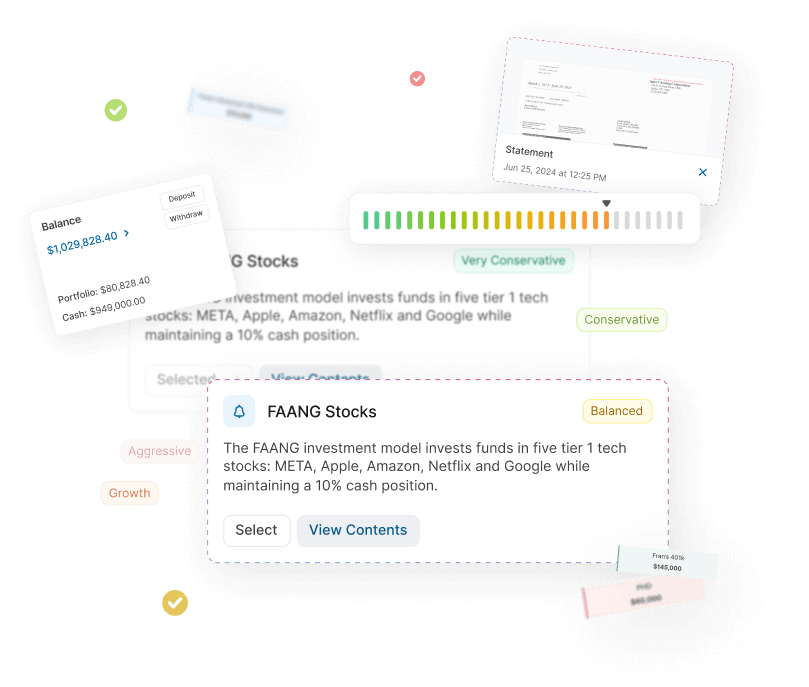
Demo Financial Advisor Software
Manage portfolios with advanced rebalancing and real-time insights.
Access customizable client reports and streamlined compliance tools.
Designed for advisors seeking efficient client and portfolio management.
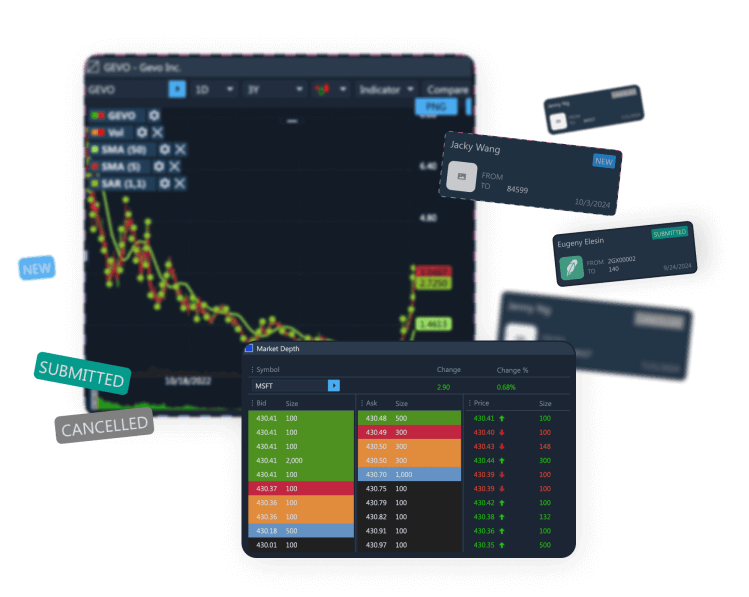
Demo Advanced Trading Platform
Test multi-asset strategies with real-time and historical data.
Analyze market depth, execute complex options, and algorithmic orders.
Ideal for refining strategies and risk management before live trading.

Demo Paper Trading Platform
Practice trading with virtual funds in real market conditions.
Simulate cash, margin, and day-trader accounts to gain experience.
Perfect for honing skills in a risk-free, customizable environment.