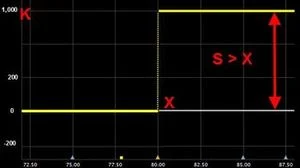
The most popular binary option type is “cash-or-nothing”. It is easy to understand:
| For example, you get $1,000 (K) if the underlying price (S) is more than strike price (X) at the expiration date. | K if S > X | 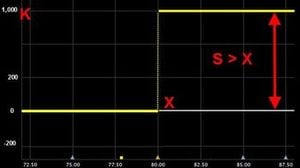 |
| You get nothing if the strike price is less than the underlying price at the expiration date | 0 if S <X | 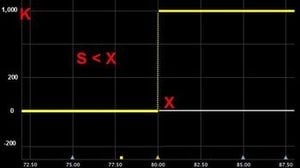 |
Another type, the “cash-or-nothing” option pays K at expiration if the option is in-the-money and 0 otherwise.
The “Asset-or-nothing” binary option is the same as “cash-or-nothing”, except for the fact that payoff is equal to the underlying price.
|
You get the underlying price (S) if the underlying price (S) is more than the strike price (X) at the expiration date. |
S if S > X | 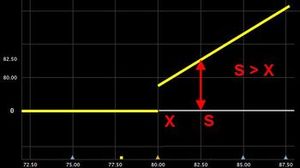 |
| You get nothing if the strike price is less than the underlying price at the expiration date. | 0 if S <X | 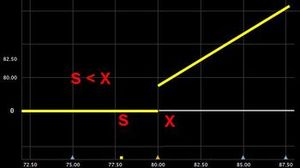 |
“Asset-or-nothing” options are not the regular type which pays the difference between strike price and underlying price: S-K.
The difference between regular and “asset-or-nothing” options types are shown below:
|
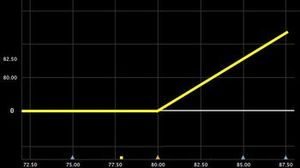
Regular (Plain Vanilla) |
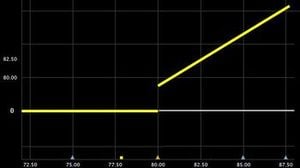
Asset-or-Nothing |
|
For in-the-money options payoff is S-K |
For in-the-money options payoff is S |
 |
 |
Of course, this is not the complete list of binary option types. For instance, there are 28 different types of binary barrier options which exist; both “cash-or-nothing” and “asset-or-nothing”. Some of them will be covered in the next article.
ETNA Software has recently created the software for binary options.

Demo Financial Advisor Software
Manage portfolios with advanced rebalancing and real-time insights.
Access customizable client reports and streamlined compliance tools.
Designed for advisors seeking efficient client and portfolio management.
Demo Advanced Trading Platform
Test multi-asset strategies with real-time and historical data.
Analyze market depth, execute complex options, and algorithmic orders.
Ideal for refining strategies and risk management before live trading.

Demo Paper Trading Platform
Practice trading with virtual funds in real market conditions.
Simulate cash, margin, and day-trader accounts to gain experience.
Perfect for honing skills in a risk-free, customizable environment.